Training LLMs: Building Your Own Local Rig
My journey into Large Language Models (LLMs) began with the excitement of seeing ChatGPT in action. I started by exploring diffusion models, drawn to their ability to create beautiful visuals. However, working on an M1 chip had its limitations, which motivated me to build a custom rig with an NVIDIA 4090 GPU. As I continued to explore LLMs and experimented with multi-agent systems, I came to realize the importance of mastering the fundamentals. This realization led me to focus on training LLMs from scratch—not just to use them but to deeply understand how they function and evolve.
Rig Evolution
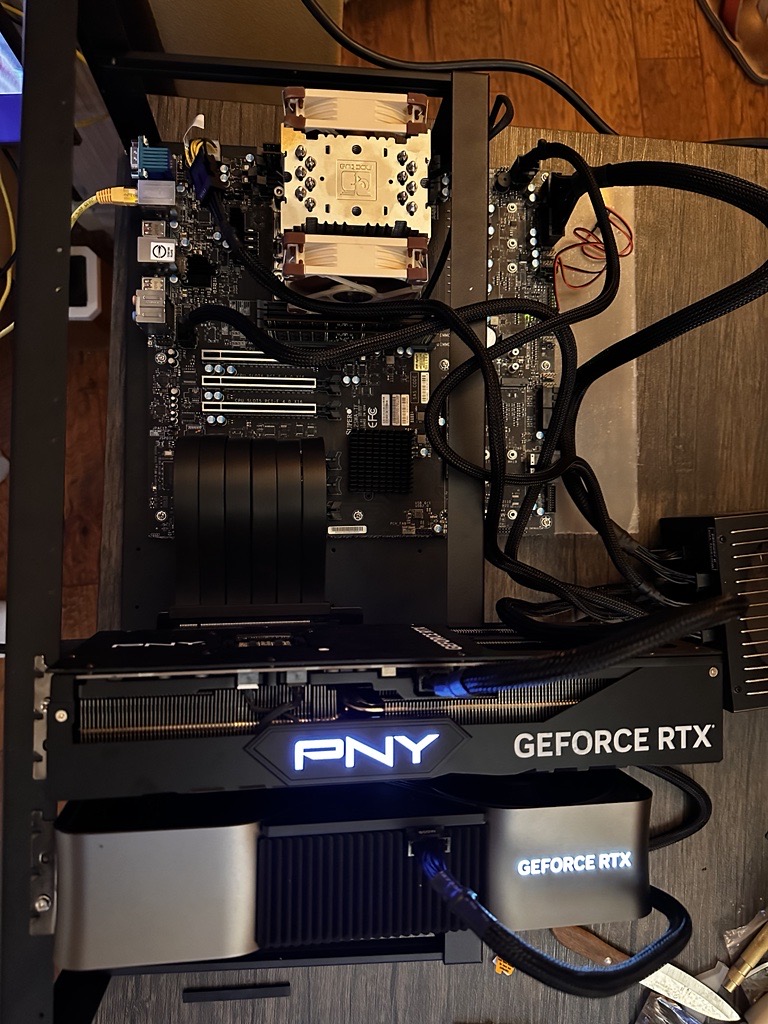
Note: This setup is capable of training models with up to 1 billion parameters; however, it performs better with ~500 million parameter models to achieve higher model utilization (MFU).
- Initial Build: Rig with 2x NVIDIA 4090 GPUs.
- Upgraded Build: Rig with 4x NVIDIA 4090 GPUs.
Here’s a comprehensive guide to building a custom rig tailored for LLM training.
Total Cost: This entire setup cost approximately $12,000 USD. This may not be cost effective but I wanted to get hands on and do more experimentation.
You can always go with cloud for a fraction of the cost . Please check out https://lambdalabs.com/ , https://hyperbolic.xyz/ and several others
Next Step: My journey into LLMs
1. Planning Your Build
-
Define Your Objectives: Determine the scale and type of models you want to train. Smaller models may work with limited resources, but larger architectures demand higher computational power.
-
Budgeting: Set a realistic budget to balance performance with cost. Note that high-end components, especially GPUs, can be costly.
2. Selecting Hardware Components
-
Motherboard: Choose a server or workstation board, primarily for the number of PCIe lanes and compatibility with multiple GPUs. I recommend the SuperMicro M12SWA-TF. While it’s an excellent board, its noisy chipset fan may need replacement with a beefier heatsink and a Noctua fan.
-
CPU: Opt for a robust processor like the AMD Threadripper PRO 5955WX. The primary reason for choosing this CPU is its 128 PCIe lanes, allowing you to connect multiple GPUs without bandwidth constraints.
-
Memory (RAM): Ensure compatibility between your RAM and motherboard. A setup with 128 GB memory is recommended for large datasets and computational tasks.
-
GPUs: NVIDIA 4090 GPUs are ideal for LLM training due to their advanced Ada architecture. Key benefits include:
- 24 GB VRAM: Sufficient for handling large models and datasets.
- BFloat16 Performance: Fourth-generation tensor cores deliver exceptional performance with up to 330 TFLOPS of bfloat16 precision, ensuring efficient computation for AI workloads.
- CUDA Cores: 16,384 CUDA cores ensure unparalleled parallel processing capabilities.
- Architecture Advantages: Enhanced ray tracing, Shader Execution Reordering, and DLSS 3 technology for improved efficiency. Well this may not directly provide benefit but because this is a consumer grade card these features enabled having support for more advanced features such as bfloat16 and event float8 training support also the sheer number of cuda cores.
- Flash Attention: Previous generations such as 3090 dont support latest Flash attentions
A setup with 4x NVIDIA 4090s, connected using riser cables like this one, offers top-notch performance for training LLMs. Several people discourage using just the cable due to potential PCIe errors, but in my experience, it worked flawlessly without any issues.
-
Storage: Invest in high-capacity storage solutions. My setup includes 6 TB of NVMe SSDs for blazing-fast access and 8 TB of HDD storage for archiving.
-
Power Supply: Dual PSU setups are often necessary for high-power builds. I used 2x 1500 Watt Be Quiet PSUs (Amazon link). Each PSU powers two GPUs, with one also powering the motherboard and CPU. Each GPU was consuming around 450W of power using DDP 500M model for ~10 days
-
Case/Frame: For mounting, I recommend this case, which accommodates multiple GPUs and robust cooling.
-
Cooling System: Replace noisy chipset fans with heatsinks like this one for quieter and more efficient cooling.
-
Motherboard Baseboard: Use a baseboard like this one for proper fitting in the case.
3. Assembling the Rig
-
Dual PSU Setup: When using two power supplies, ensure one powers the motherboard and CPU, while each PSU powers two GPUs. Specialized adapters can help synchronize their power-on sequence. This needs 30 AMP circuit, you might able to connect it to 2 different breakers but this is not recommended.
-
Compatibility Check: Ensure all components are compatible to avoid assembly issues.
-
Physical Assembly: Carefully install components, paying special attention to GPU placement and spacing for optimal airflow.
-
Cable Management: Organize cables neatly to improve airflow and simplify maintenance.

4. Software Configuration
-
Operating System: Use a Linux-based OS (e.g., Ubuntu), known for its stability and suitability for machine learning tasks.
-
Drivers and Dependencies: Install the latest GPU drivers, CUDA, and cuDNN libraries to maximize GPU performance.
-
Machine Learning Frameworks: Set up frameworks like PyTorch or TensorFlow, essential for model training.
-
Custom Kernel: I used a custom kernel from Tinygrad to enable P2P communication between GPUs, further enhancing performance.
5. Training Large Language Models
-
Data Preparation: Curate, clean, and preprocess datasets to ensure high-quality inputs for training.
-
Model Selection: Choose architectures like Llama2 or GPT, tailored to your hardware and training goals.
-
Training Process: Initiate training, monitor resource utilization, and adjust configurations as needed for optimal results.
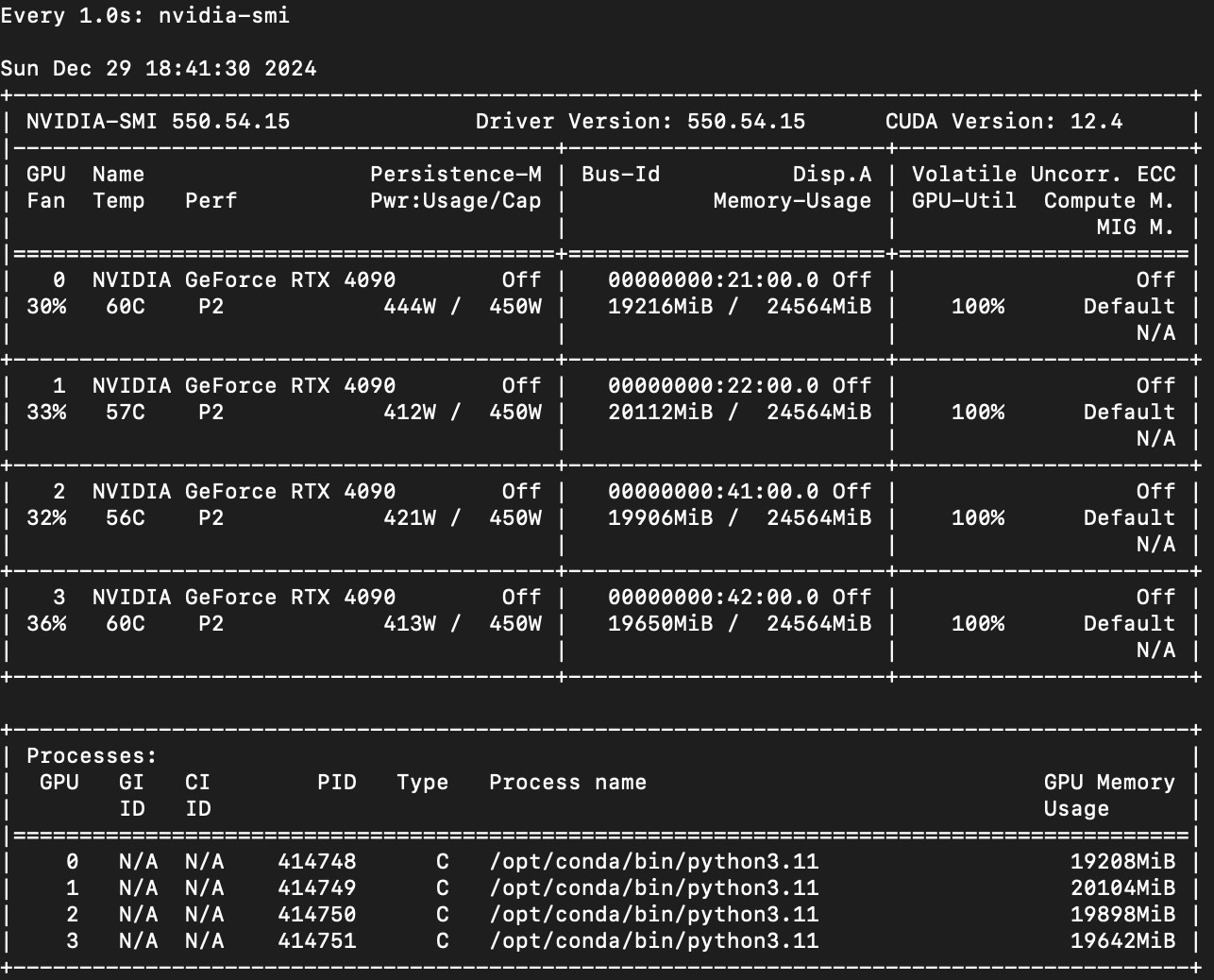
6. Optimization and Scaling
-
Multi-GPU Training: Use distributed training techniques such as Distributed Data Parallel (DDP) or ZeRO to fully utilize multiple GPUs.
-
George’s Hack: Leverage the kernel patch by George Hotz to enable peer-to-peer (P2P) communication for NVIDIA 4xxx GPUs, overcoming the lack of official support.
-
Performance Tuning: Optimize hyperparameters, batch sizes, and learning rates to achieve better convergence and efficiency.
7. Maintenance and Monitoring
-
Regular Updates: Keep your system and software updated to leverage the latest optimizations and security patches.
-
System Monitoring: Use tools like NVIDIA’s nvidia-smi or Prometheus to track system health, utilization, and temperature.
Key Insights and Tips
-
Hardware Alternatives: While GPUs like the A100 or H100 provide higher VRAM, consumer GPUs such as the 4090 offer excellent performance for cost-conscious setups.
-
Cloud Considerations: On-premise rigs are ideal for long-term projects and experimentation, but cloud solutions offer flexibility for short-term tasks.
-
Community Resources: Explore tutorials from experts like Andrej Karpathy and guides from Hugging Face for additional insights.
Building a rig for LLM training is a challenging but rewarding endeavor that opens up opportunities to push the boundaries of AI development. With careful planning and execution, your custom setup can become a powerful tool for exploring the vast landscape of machine learning.